WATER POTABILIZATION
POTABILI is a high-tech potabilization plant, the result of years of experience, development and research.
It's the first world HDPE (High Density Polyethylene) modular plant.
Its main benefits are: the logistics of the transfer, the modularity of the processes, the useful life of its components, the performance in terms of flow, the economy in maintenance and initial investment.
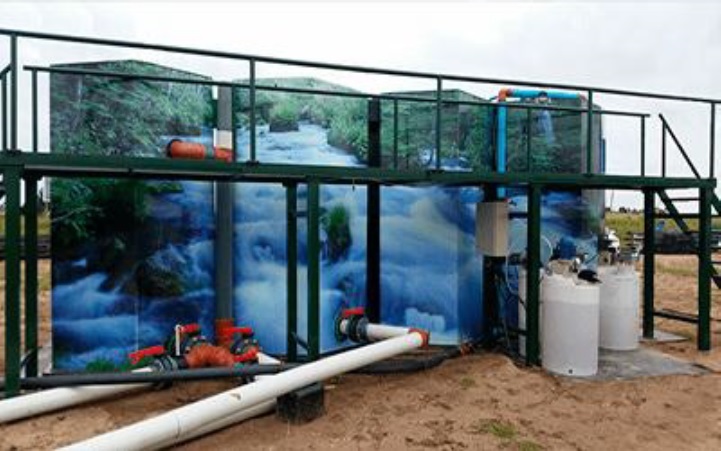
The component stages of the process are carried out in independent reactors, so that each stages is located in reactor, they are hexagonal prismatic, equal in shape and size of one meter long.
This new modular plant for the purification of fresh water, superficial or underground, is easily transportable, built in HDPE (which provides a solution against oxidizing agents), with the almost null execution of civil works, designed in such a way that the individual processes are carried out in hexagonal reactors (that optimize said processes), which leads to a minimization of the occupied spaces, and the obtaining of large volumes of potable water, compared to traditional plants, so installation cost are drastically reduced as well as maintenance costs, where a single operator without major difficulty can become responsible for the management and maintenance of the plant. Allowing in the future to expand without limits, the purification flows, without interrupting the distribution services to the population.
MODULARITY: the design and design of individual modules of hexagonal prisms of the same shape and size that contain each of the processes separately, allow the configuration of an original mosaic, and from it, incorporate modification (extensions) in the treatment by adding new modules for any stages of the treatment.
TRANSPORTABILITY: the external dimension, the shape, the size of the hexagonal prisms and their weight give the plant great ease of transport in standard containers (land, sea, air), a situation that is not achieved with conventional plants, even if they are compact, due to the minimum height that must be respected in the latter, when designed in a single unit.
ADAPTABILITY: the Potabili plant, in its minimum expression (AMM - Minimum Modular Assembly) is made up of four hexagonal prisms, each containing the basic treatment processes and obtaining a flow rate of 25 cubic meters per hour. In case the required demand grows regardless of the amount it is possible to attend the new flow; adding more reactors to the existing installation, in this way the plant presents an adaptability to growth in an optimum and unlimited way, whatever the magnitude of the flow required to treat.
ECONOMY: the saving of investment and operation costs are the result of the design and design of individual modules of hexagonal prisms, but in high density polyethylene (HDPE), equal in shape and size that allow the configuration of an original open mosaic, its modification with the incorporation of new modules. With a minimum investment is achieved, an "upgrade" that will also make possible a reduction in the dosage of chemical products and will cause simultaneously higher sedimentation loads and higher filtration rates, all resulting in an improvement in the quality of the water produced, an increase in treatment capacity and a significant saving in operating costs, because it should not require more human resources for the same functions.
The purification of water is a process composed of several stages, each of which is carried out in a reactor, in such a way that water is obtained that is absolutely suitable for human consumption
STAGE 1:
QUICK MIX
It corresponds to the stage during which coagulation takes place, that is to say, the breakdown of the general equilibrium of the contents originally brought by raw water (organic and inorganic matter, turbidity and color particles, bacteria, viruses, protozoa, phytoplankton, zooplankton, colloids, heavy metals, etc.) and the birth of a new balance characterized by the creation and formation of the micro-floc.
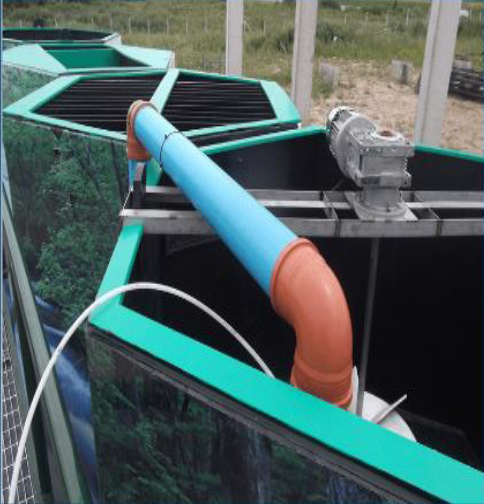

STAGE 2:
FLOCCULATION
The main purpose of flocculation is to transform the smallest destabilized particles into larger agglomerates called "flocs".
Mechanical flocculation is developed through three stages in series and separate compartments.
Hydraulic flocculation is ideal to complement the first three compartmented stages, generating a small and stable velocity gradient (G) of constant flow velocity, preparing the entrance of water to the sedimentation process.

STAGE 3:
SEDIMENTATION
This function is considered to be of high rate, of ascending flow through parallel flat plates, arranged in arcsinusoical from with inclination 60º with the horizon in its flat trajectory.

STAGE 4:
FILTER
The filter fluid of the filters will be selected according to the treatment. In normal or general situations, the mantle will be sand and gravel. But the use of a multiple layer of sand and anthracite, or a bed of granular activated carbon is not ruled out.

STAGE 5:
DESINFECTION
It is carried out through the chlorine dosing by means of 10% sodium hypochlorite solution. A pump system is used diaphragm dosing - solution tank, and contact tank. It is evident that the disinfection, of the water that has gone through the processes of treatment, aims at the destruction of the causative organisms of diseases present in the water - which have crossed the barrier of treatment - and maintain some residual power for water protection drinking water in feeders or pumping lines, in distribution networks and in reservations. In the design of the executive project will be analyzed according to the characteristics and to total demand.

TANK LAYOUT
Flexibility to "assemble" the mosaic of hexagonal prisms containing each process, according to the space requirements.
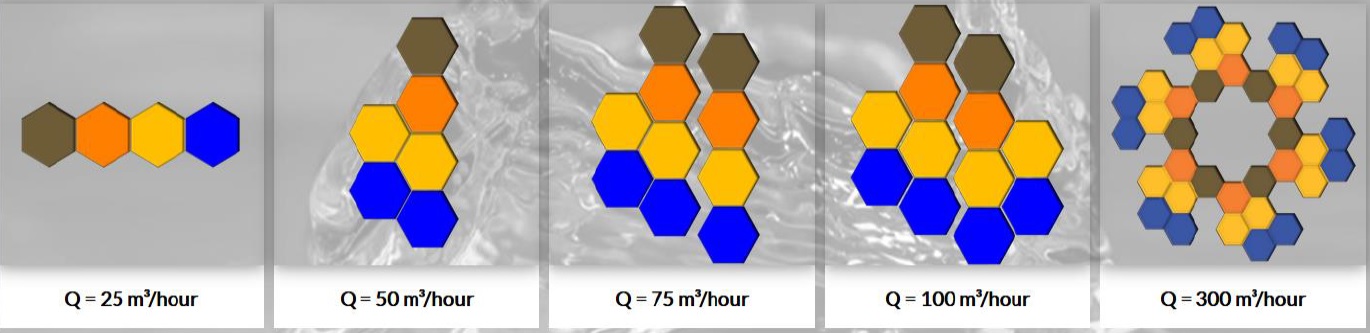
TANKS

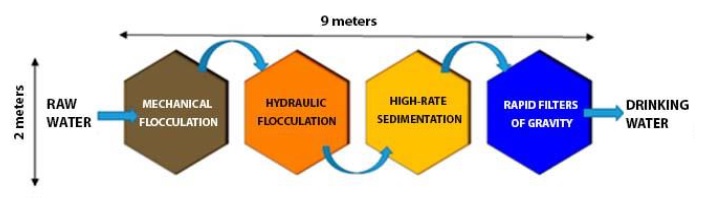
TANKS






